How To Read A Balance Sheet

Content

In other words, it’s an important document that serves as a snapshot of a business’ finances at a specific point in time by comparing what you own to what you owe. On the other hand, noncurrent assets, also called long-term assets, are those that you’ll hold onto for a year or longer.
We also show how the same transaction affects specific accounts by providing the journal entry that is used to record the transaction in the company’s general ledger. This can help you determine if you should apply for an unsecured business loan or more traditional bank debt. So how exactly do these numbers magically appear on the balance sheet? Comparing current assets to current liabilities is called the current ratio. Property, Plant, and Equipment (also known as PP&E) capture the company’s tangible fixed assets.
How would you distinguish equity from liability?
Equity is a form of ownership in the firm and equity holders are known as the ‘owners’ of the firm and its assets. Liabilities are amounts that are owed by the firm.
For instance, Johnson & Johnson’s balance sheet for December 31, 2020, lists $174 billion in assets. In 2019, it recorded $157 billion—they acquired $17 billion in assets over that period. The liabilities section is also broken into two subsections—current liabilities and all others.
Examples Of Equity
A profitability ratio measures how well a business is able to use its assets to produce a profit. In addition, a company may rely heavily on operating leases for equipment it uses, but these leases are not listed as a liability on a balance sheet. As any equipment lease attorney could explain, operating leases are in effect long-term payment obligations that are akin to, if not actual, secured borrowings.
The information shows the results or consequences of prior management decisions. In addition, analysts use the information to make predictions that may have a direct effect on decisions made by users of financial statements. Management’s analysis of financial statements primarily relates to parts of the company. Using this asset = liabilities + equity approach, management can plan, evaluate, and control operations within the company. Management obtains any information it wants about the company’s operations by requesting special-purpose reports. It uses this information to make difficult decisions, such as which employees to lay off and when to expand operations.
What Does A Balance Sheet Tell You About A Business?
You must charge more than the unit cost of the product to be profitable. Liabilities might be broken out into short-term — those that you’ll pay off in 12 months or less, such as payroll and credit lines — and long-term liabilities, such as mortgages and bonds. Knowing how to read a balance sheet can help an investor or lender understand a business. However, a balance sheet should neither stand alone nor be taken at face value. Diligence about categories on the balance sheet is critical not only to discovering issues, but also to gaining comfort with the way the business has operated.
What are current liabilities?
Current liabilities are a company’s short-term financial obligations that are due within one year or within a normal operating cycle. … Examples of current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term debt, dividends, and notes payable as well as income taxes owed.
Investors also use financial ratios generated from these three statements to help them valuate a business and determine if it fits their investment strategy and risk tolerance. The balance sheet has three sections, each labeled for the account type it represents. Balance sheets can follow different formats, but they must list the three components of the accounting equation.
The way a company accounts for common stock issuances can seem complicated; however, at its most basic level, the move simply involves crediting or increasing stockholders’ equity. For this exercise, it’s helpful to think of stockholders’ equity as what’s left when a company has paid all its debts, sometimes referred to as book value. Assets are things that could increase the value of a company over time, while liabilities are debts that must be paid or goods and services obligations that must be fulfilled. Investors may wonder where common stock fits into the equation. It is not possible to calculate dividends from a balance sheet by itself. If the company does not list dividends, obtain their income statement.
Income And Retained Earnings
The balance sheet is one of the three basic financial statements that every owner analyzes to make financial decisions. Owners also review the income statement and the cash flow statement. Attributing preferred shares to one or the other is partially a subjective decision, but will also take into account the specific features of the preferred shares.
For a bank you represent a liability, in Tech you are an asset. (Equity = Assets – Liabilities)
— jhvh111 (@jhvh111) November 23, 2021
For businesses that offer product warranties, such a guarantee is considered a noncurrent liability. In the life of any business entity, there are countless transactions. Each can be described by its impact on assets, liabilities, and equity. Note that no properly recorded transaction will upset the balance of the accounting equation. Compare the current reporting period with previous ones using a percent change analysis. Calculating financial ratios and trends can help you identify potential financial problems that may not be obvious.
Balance Sheet Example
The assets are listed, moving downward, in the order of their ease of liquidation. Cash is already liquid, accounts receivable are more liquid than inventory, and so on. Assets and liabilities are determinable values, meaning they are subject to measurement and calculation.
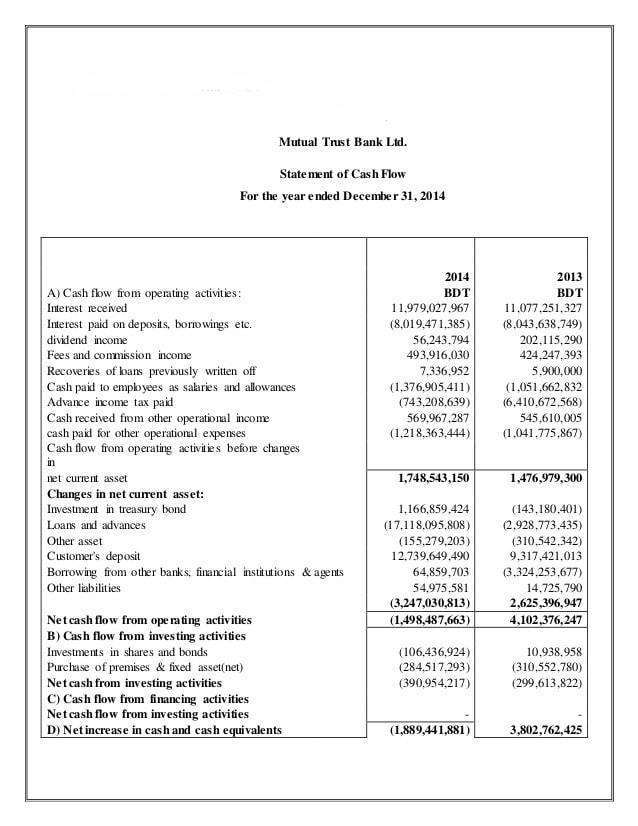
In the asset sections mentioned above, the accounts are listed in the descending order of their liquidity . Similarly, liabilities are listed in the order of their priority for payment.
Video Explanation Of The Balance Sheet
In many cases, the carrying value of an asset and its market value will differ greatly. If the asset is valued on the balance at market value, then its book value is equal to the market value. Cash, receivables, and liabilities are re-measured into U.S. dollars using the current exchange rate. The Working Capital ratio is similar to the Current Ratio but looks at the actual number of dollars available to pay off current liabilities. Like the current ratio, it provides an indication of the company’s ability to meet its current debt.
Owner’s draws and expenses (e.g., rent payments) decrease owner’s equity. Like revenue accounts, expense accounts are temporary accounts that collect data for one accounting period and are reset to zero at the beginning of the next accounting period.
Ang math nalang na alam ko is asset = liabilities + equity hindi a4 + b4 = (a2 + b2)2 – 2a2b2 = (a2 + √2ab + b2)(a2 – √2ab + b2)!!!
— ingrid (@valeriebalendez) December 4, 2017
This financial statement is used both internally and externally to determine the so-called “book value” of the company, or its overall worth. Your bank account, company vehicles, office equipment, and owned property are all examples of assets. If your accounting is accurate, as you should hope it is, your balance sheet will always balanced. That means if you compare assets with the sum of your liabilities and equity, the two should always equal one another.
Assets and liabilities form a picture of a small business’s financial standing. The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time.
The aggregate difference between assets and liabilities is equity, which is the net residual ownership of owners in a business. Capital or shareholders’ equity is the amount the owners invested in the company’s stock, plus or minus the company’s earnings or losses since the inception of the business. For every amount of value that you receive, you in turn, give an amount of value as payment, keeping the company’s books in balance. A Balance Sheet is a statement showing the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity of a business. It provides detailed information in a specifically defined format. From the income statement, use the net profit figure from the latest period. If the net change in retained earnings is less than the latest net profit, there was a dividend payout.
It also keeps track of your business’ assets, liabilities, and equity and gives you the data at any given point in time. For this reason, it’s also known as the statement of financial position. Here, the owner’s value in assets is $100, which is the company’s equity. Equity in accounting is often classified as retained earnings, treasury stocks, or a company’s book value. This figure is crucial to understand a business’ economic condition.
A deferred expense or prepayment, prepaid expense , is an asset representing cash paid out to a counterpart for goods or services to be received in a later accounting period. For example, if a service contract is paid quarterly in advance, at the end of the first month of the period two months remain as a deferred expense. In the deferred expense, the early payment is accompanied by a related, recognized expense in the subsequent accounting period, and the same amount is deducted from the prepayment. Assets on a balance sheet are classified into current assets and non-current assets. The balance sheet summarizes a business’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders ‘ equity. A balance sheet reports a company’s financial position on a specific date. The balance sheet highlights the financial position of a company at a particular point in time .
Each of the three segments on the balance sheet will have many accounts within it that document the value of each. Accounts such as cash, inventory, and property are on the asset side of the balance sheet, while on the liability side there are accounts such as accounts payable or long-term debt. The exact accounts on a balance sheet will differ by company and by industry. A company’s assets must equal their liabilities plus shareholders’ equity.
Form 424B5 OFS Credit Company, Inc. – StreetInsider.com
Form 424B5 OFS Credit Company, Inc..
Posted: Wed, 01 Dec 2021 12:21:07 GMT [source]
Additional resources for managing your practice finances will appear in future issues of the PracticeUpdate E-Newsletter and on APApractice.org. The current ratio, which is the simplest measure and is calculated by dividing the total current assets by the total current liabilities. A value of over 100% is normal in a non-banking corporation.
It’s up to you to make sure you’re business is as strong as it can be. And one of the most important ways to do that is by understanding how to look at your business metrics to tease out insights and feedback. Here’s a simplified version of the balance sheet for you and Anne’s business. A few days later, you buy the standing desks, causing your cash account to go down by $10,000 and your equipment account to go up by $10,000. Right after the bank wires you the money, your cash and your liabilities both go up by $10,000. Now let’s say you spend $4,000 of your company’s cash on MacBooks.
- Assets are anything valuable that your company owns, whether it’s equipment, land, buildings, or intellectual property.
- This can sometimes make it difficult to understand what is listed in each section.
- By using the temporal method, any income-generating assets like inventory, property, plant, and equipment are regularly updated to reflect their market values.
- Publicly-owned businesses must file standardized reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission to ensure the public has access to their financial performance.
- A troubling example involves a company with a large amount of accounts receivable due from various medical insurance companies.
Remember —the left side of your balance sheet must equal the right side (liabilities + owners’ equity). Understanding the different types of financial documents and the information each contains helps you better understand your financial position and make more informed decisions about your practice. This article is the first in a series designed to assist you with making sense of your practice’s financial statements.

Liabilities are the debts owed by a business to others–creditors, suppliers, tax authorities, employees, etc. They are obligations that must be paid under certain conditions and time frames. A business incurs many of its liabilities by purchasing items on credit to fund the business operations. The balance sheet contains statements of assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity. A current ratio of 2.00, meaning there are $2.00 in current assets available for each $1.00 of short-term debt, is generally considered acceptable.
Author: Nathan Davidson



